AMD has made new moves in the field of GPU technology, and its next-generation UDNA/RDNA5 architecture graphics card is expected to achieve a new leap in ray tracing and animation performance.
In the GPUOpen blog post, AMD demonstrates how DGF (Dense Geometry Format) shapes the performance of GPUs in modern animation and ray tracing, and plans to integrate hardware-level capabilities into future GPUs.
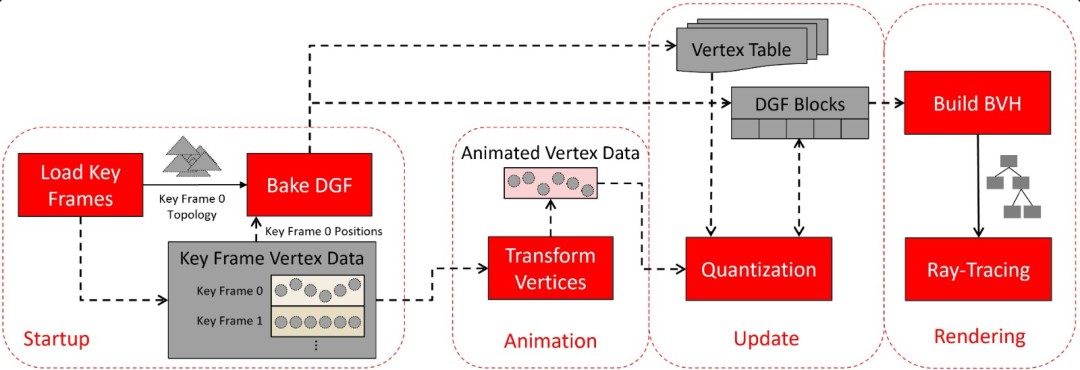
The core of DGF technology lies in the efficient processing of geometric data. When traditional GPUs deal with animation geometry, they need to process a large number of triangle meshes, which not only occupies a large amount of memory bandwidth, but also increases the computing burden.
And DGF greatly reduces the amount of data by segmenting large triangle meshes into small "mesh blocks" and storing the data of each block in a dense format.
This compression method not only saves memory bandwidth, but also allows the GPU to process geometric data more efficiently.
In terms of ray tracing, DGF has more obvious advantages. ray tracing technology requires frequent reconstruction of BVH (boundary volume hierarchy), while data in DGF format can be directly understood by the GPU, thereby reducing the overhead of reconstruction of BVH.

This not only reduces resource consumption, but also improves ray tracing performance. Currently, DGF processing is mainly done in AMD's computing shader unit, but in the next generation of UDNA architecture graphics cards, DGF is expected to be integrated into fixed function hardware units, thereby achieving faster animation processing speeds.
In addition, DGF compression technology also reduces resource overhead, allowing more geometric data to be stored in the GPU cache, further reducing latency and improving performance.














